Unified Smoking Feature Generator
Background
The purpose of the Unified Smoking Feature Generator is to generate smoking related features based on different types of available smoking information. It was based on THIN and KPSC databases.
Input Signals
The generator currently require the following signals (it doesn't depend anymore on the THIN smoking_quantity signal):
| Signal | THIN | KPSC | KPNW |
|---|---|---|---|
| Smoking_Status | v | v | v |
| Smoking_Quit_Date | v | x | v |
| Pack_Years | x | v | x |
| Smoking_Intensity [Cigs/Day] | v | x | v |
Smoking_Duration [Years] |
x | v | v |
Note: Every repository should have those signals, even if they are not (in that case they should be empty signals) The Smoking_Status signal is a categorical signal, with the following values: Never, Passive, Former, Current, Never_or_Former. Extraction of the status in THIN is described in the Appendix
Output Features
Boolean features: 1. Current_Smoker 2. Ex_Smoker 3. Never_Smoker 4. Passive_Smoker 5. Unknown_Smoker 6. NLST_Criterion - 1 if age between 55 to 74, pack years > 30, time since quitting < 15 years. ** features:** 1. Smok_Days_Since_Quitting - For current smokers - 0, For Former smokers, time since quitting, for Never Smokers - time since birth 2. Smok_Years_Since_Quitting - same as previous, but in years 3. Smok_Pack_Years_Max - Maximal report of pack years (pack years if available) if not, it is estimated (and can be corrected with intensity 4. Smok_Pack_Years - the same as Smok_Pack_Years_Max 5. Smok_Pack_Years_Last - Last pack years report (without estimation) 6. Smoking_Intensity - Number of pack per day 7. Smoking_Years - Smoking duration.
Config Example
Logic Explanation
The most basic information we need to extract is smoking status on different time points The logic is based on the paper: Development of an algorithm for determining smoking status and behaviour over the life course from UK electronic primary care records https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5217540/pdf/12911_2016_Article_400.pdf The workflow is built from the following methods: 1. genFirstLastSmokingDates - For each status find the first time and last time it appears. This is the input for setting the status at each smoking status report. 2. genSmokingStatus - generate for each point in smoking status vector a corrected smoking status. See Figure 1 3. genSmokingRanges - Build Smoking status ranges 4. genLastStatus - Set the Boolean smoking status features (take the last status according the the previous method output) 5. calcQuitTime - generates Smok_Days_Since_Quitting/Smok_Years_Since_Quitting. Check that last status in the ranges vector - If former smoker, take the delta between sample time to beginning of the "former smoking" period, if Current smoker, take 0. if never smoker return time since birth date. 6. calcSmokingIntensity - returns smoking intensity (averages the smoking intensity vector). 7. calcPackYears - Set pack years according to the pack years vector. 8. calcSmokingDuration - Return duration. runs over the ranges vector and integrates the period in which the status is "Current smoker" 9. fixPackYearsSmokingIntensity - Fix pack years using smoking intensity and duration. If Intensity is unknown and pack years is known calculate intensity. Example: Taken from THIN, birth date : July 1959, sample date 05/08/2011. Marked in Grey - Input (Raw) Data
| Smoking Status | 19900315 Current | 19970227 Never | 19970227 Never_or_Former | 20060824 Never | |
| Smoking Intensity |
|
19900315 15.000000 |
19970227 0.000000 | 20060824 0.000000 | 20060824 0.000000 |
| Quit time | |||||
| Pack years | |||||
| Smoking Status Processed | 19590700 UNKNOWN_SMOKER | 19900315 CURRENT_SMOKER | 19970227 EX_SMOKER | 19970227 EX_SMOKER | 20060824 EX_SMOKER |
| Smoking Status Ranges | 19590700-19781231 UNKNOWN_SMOKER | 19790101-19930904 CURRENT_SMOKER | 19930905-20110805 EX_SMOKER | ||
| Intensity Out: | 15 | ||||
| Duration Out: | 14.684932 | ||||
| Quit time: | 17.926027 | ||||
| Pack years: | 11.013699 |
Appendix - Extracting Smoking Status in THIN
In THIN database, smoking status is extracted from Read codes.
The mapping from codes to status is taken from "Development of an algorithm for determining smoking status and behaviour over the life course from UK electronic primary care records:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5217540/pdf/12911_2016_Article_400.pdf
I have noticed that there are a lot of "collisions" in the smoking status vector when using this mapping (meaning two different status in the same date) - ~10%.
After removing non-conclusive Read codes - this was reduced to ~0.5%.
When the old THIN smoking feature generator was used in a simple LR model for lung cancer AUC was improved in 1 point.
See original and modified mapping in the table below.
smoking_readcodes_combined.csv
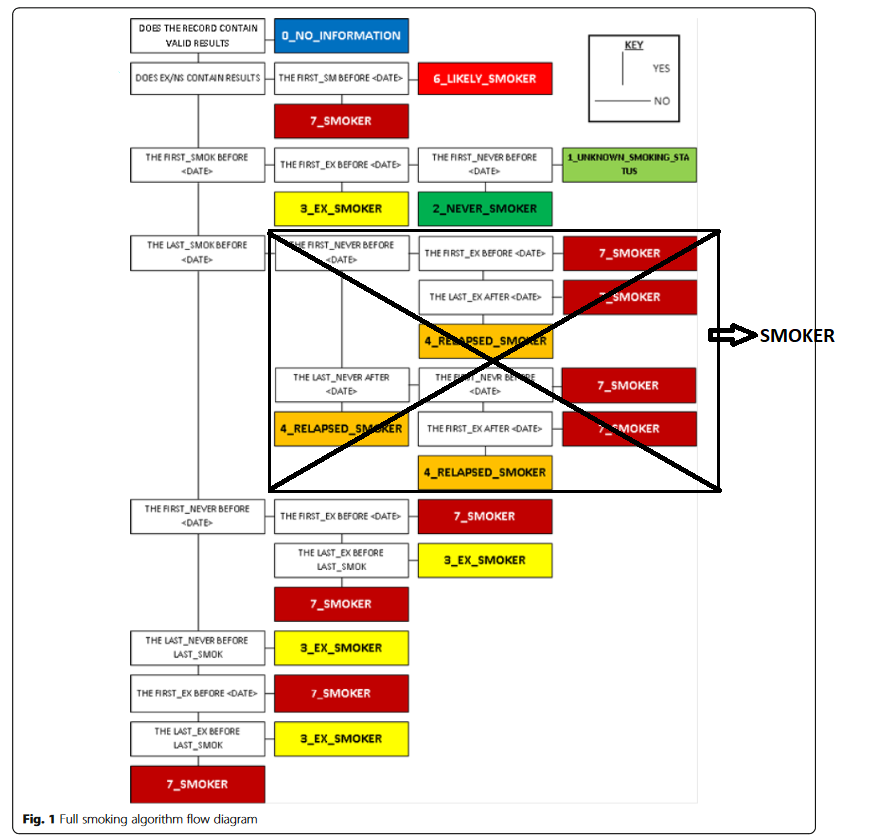 Figure 1 - Logic for setting the smoking status.
The code that generates the smoking vectors in THIN:
http://bitbucket:7990/projects/MED/repos/gensmoking/browse
Figure 1 - Logic for setting the smoking status.
The code that generates the smoking vectors in THIN:
http://bitbucket:7990/projects/MED/repos/gensmoking/browse